Contra Asset Account Definition
Content

Treasury Stock AccountTreasury Stock is a stock repurchased by the issuance Company from its current shareholders that remains non-retired. Moreover, it is not considered while calculating the Company’s Earnings Per Share or dividends. It’s not unusual for an owner to have multiple entities that do business together. In a distressed situation, is the owner going to pay back the receivable due from one of his companies to the next?
- Contra Equity Account – A contra equity account has a debit balance and decreases a standard equity account.
- Although you may be familiar with the normal balance requirements of each classification, a contra account will have the opposite requirement.
- The balance sheet would report equipment at its historical cost and then subtract the accumulated depreciation.
- A company may decide to buy back its shares when management feels the stock is undervalued or because it desires to pay stock dividends to its shareholders.
- It offsets the balance of the related account, which means when the corresponding account is positive, a contra account will be negative.
- A contra account is used in order to better portray the relationship between certain debits and credits within the overall financial structure of an entity.
It also made life much easier when it was time to report taxes. The totals show the net effect on the accounting equation and the double-entry principle, where the transactions are balanced. Equity accounts record the claims of the owners of the business/entity to the assets of that business/entity.Capital, retained earnings, drawings, common stock, accumulated funds, etc. The Profit and Loss Statement is an expansion of the Retained Earnings Account. It breaks-out all the Income and expense accounts that were summarized in Retained Earnings. The Profit and Loss report is important in that it shows the detail of sales, cost of sales, expenses and ultimately the profit of the company.
General Ledgers
For instance, a contra account that relates to an accounts receivable is called a contra asset account. These transactions are reported in one or more contra revenue accounts, which usually have a debit balance and reduces the total amount of the company’s net revenue. The same is true for other asset accounts like accounts receivable. Accounts receivable is rarely reported on the balance sheet at its net amount. Instead, it is reported at its full amount with an allowance for bad debts listed below it. Maybe more importantly, it shows investors and creditors what percentage of receivables the company is writing off. In an accounting system, ledger accounts are designed to contain only similar transactions and/or balances.
- To report the real value of the financial statement, you will need to record the amount you can reasonably estimate that will probably effect the financial statement classification.
- Some basic examples of contra accounts are bad debt and depreciation.
- Treasury stock shows the amount spent by a business for repurchasing a company’s shares from investors.
- A liability that is recorded as a debit balance is used to decrease the balance of a liability.
- These daybooks are not part of the double-entry bookkeeping system.
- A Contra account is an account that appears as a subtraction from another account on balance sheet of a company.
- Credit a contra-account “Allowance for Bad Debts” on the Balance Sheet.
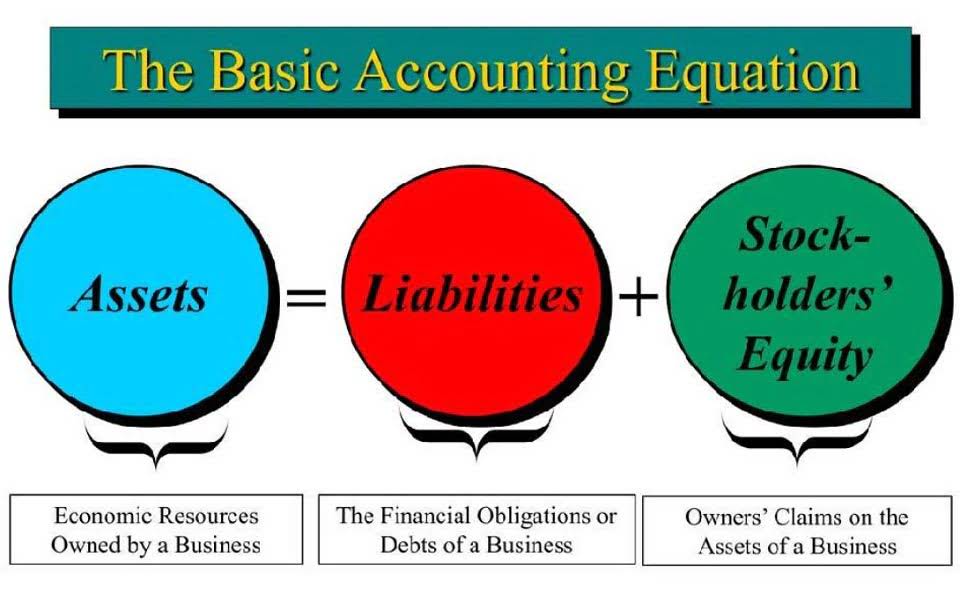
An account whose value offsets the value of an equivalent account. For example, two firms may have contra accounts in which each owes the other money. They might agree to offset the mutual debt and make a single payment to whichever is owed more. Perhaps the most common example of a contra account is an asset’s depreciation, which is subtracted from its original price to calculate its book value. In this case, the depreciation and the original price are contra accounts with respect to each other. This use of the terms can be counter-intuitive to people unfamiliar with bookkeeping concepts, who may always think of a credit as an increase and a debit as a decrease.
When Correct Account Balances May Not Be Normal Generally, an account balance that is not normal is incorrect, but there are exceptions. For example, if a company overdraws its bank account, the Cash account will have a temporary credit balance.
Allowance For Accumulated Depreciation
Most companies rely heavily on the profit and loss report and review it regularly to enable strategic decision making. The Equity section of the balance sheet typically shows the value of any outstanding shares that have been issued by the company as well as its earnings. All Income and expense accounts are summarized in the Equity Section in one line on the balance sheet called Retained Earnings. This account, in general, reflects the cumulative profit or loss of the company.
What account is capital?
In accounting, a capital account is a general ledger account that is used to record the owners’ contributed capital and retained earnings—the cumulative amount of a company’s earnings since it was formed, minus the cumulative dividends paid to the shareholders.
However, it must be understood that the concept of the contra account does not always involve a credit offsetting a debit. The basic function of this type of account is simply to be an opposite of another account. This means that an account showing a debit would be a type of contra account usually known as a contra-liability account. By the same token, an account with a credit would be balanced by a contra-asset account.
The Contra Liability Account
This method uses the initial purchase value and subtracts the accumulated depreciation value for the time period to result in the total value of the equipment after its use. Outstanding SharesOutstanding shares are the stocks available with the company’s shareholders at a given point of time after excluding the shares that the entity had repurchased. It is shown as a part of the owner’s equity in the liability side of the company’s balance sheet. This account is not classified as an asset since it does not represent a long term value. It is not classified as a liability since it does not constitute a future obligation. These accounts can be listed based on the respective asset, liability, or equity account to reduce their original balance.
Let’s say you have a truck worth $20,000 that will last five years. If you depreciated it evenly you would take $20,000, divide it by 5 and expense $4,000 each year. On the balance sheet you would list the asset at $20,000 then show the $4,000 in accumulated depreciation being subtracted from it for a net value of $16,000. Accumulated depreciation is a contra account because it subtracts from the asset.
Contra Revenue Account
These are transactions that are recorded between cash and bank accounts. It shows deductions from the revenue of a company, which results in net revenue. Discount on payables accounts are some of the accounts that can be considered contra liability accounts. A discount on bonds payable account is created to show the difference in the amount at which a company issues a bond and when the bond matures.
Contra accounts are a little tricky to think about when you are first starting out. Just remember that they carry an opposite balance than the other accounts in their account type. Contains the amount of sales discount given to customers, which is usually a discount given in exchange for early payments by customers. The interest expense would not be reversed since it is an actual expense recorded for the period. The following information is available from the financial records of X Company. All “mini-ledgers” in this section show standard increasing attributes for the five elements of accounting. Contra Accountmeans the account against which the Control Account’s balances settled as per the parameters defined for that Control Account.
The company may take buyback decisions if it thinks the stock is undervalued in the open market or it decides to pay dividends to shareholders. In general, a contra account is simply a means of making sure that all aspects of transactions are accounted for in an orderly and timely manner. To determine whether to debit or credit a specific account, we use either the accounting equation approach , or the classical approach . Whether a debit increases or decreases an account’s net balance depends on what kind of account it is. The basic principle is that the account receiving benefit is debited, while the account giving benefit is credited. A contra-account is a balance sheet account whose purpose is to reduce the amount of another account.
So, if the company reported receivables amounting to $100,000, the estimated 5% default rate would reduce the number of accounts receivable by $5,000. Some basic examples of contra accounts are bad debt and depreciation. Bad debt is uncollectible revenue, which offsets a doubtful receivable. The adjustment to long-term debt, on the other hand, is a contra liability account to mortgage payable that reduces the mortgage payable for long-term debt only.
Types Of Contra Accounts
Therefore, an example of a contra asset account involved with a depreciation situation seems reasonable to observe. Nova Incorporated is attempting to finalize their balance sheet in terms of the net value of their assets. At the end of the year, their assets are as follows… Nova Company valued a van at $30,000, an office building at $500,000 and office equipment at $20,000. At the same time, depreciation for the van at the end of the year ended up at $500. And the depreciation for the office equipment ended up at $1,000. Examples of contra accounts include Allowance for Doubtful Accounts, Accumulated Depreciation, and Return on Sales. The Johnson family’s purchase of furniture illustrated the effect on the financial statements for two kinds of contra accounts, revenue, and asset.
A contra account is an account with a balance opposite the normal accounts in its category. Contra accounts are usually linked to specific accounts on thebalance sheetand are reported as subtractions from these accounts. In other words, contra accounts are used to reduce normal contra account definition accounts on the balance sheet. Other contra account examples can be Allowance for Doubtful Accounts , Bond discounts, which represent contra liability account, i.e. decrease bond payable account. Accumulated depreciation is accounted on the credit side and has credit balance.

Periodic financial statements report the impact of the story and are used by leaders of a firm or industry to analyze performance, plan, and respond. Contra revenue account, which is used to record the net amounts and usually has a debit balance, as opposed to the revenue account that records the gross amounts. A contra account is an account whose balance is the opposite of a corresponding account.
Definition Of A Contra Account?
To understand the actual value of sales, one must net the contras against sales, which gives rise to the term net sales . A contra account offsets the balance in another, related account with which it is paired. Contra accounts appear in the financial statements directly below their paired accounts. Sometimes the balances in the two accounts are merged for presentation purposes, so that only a net amount is presented.
A contra account is a ledger account related to another specific ledger account. In fact, as the name “contra” suggests, it is the opposite of a specific class of account. However, if the billing office stopped there, you would overstate your assets and net income.
These daybooks are not part of the double-entry bookkeeping system. The information recorded in these daybooks is then transferred to the general ledgers. Not every single transaction needs to be entered into a T-account; usually only the sum of the book transactions for the day is entered in the general ledger. Before the advent of computerised accounting, manual accounting procedure used a ledger book for each T-account. The collection of all these books was called the general ledger. The chart of accounts is the table of contents of the general ledger. Totaling of all debits and credits in the general ledger at the end of a financial period is known as trial balance.
The situations that contra asset accounts appear are the ones dealing with Depreciation, which will be explored below. The following are several key reasons why it can be important to include contra asset accounts on a balance sheet. This amount is typically paired with the company’s current assets on the balance sheet. When a company evaluates its financial position, a financial analyst might calculate the total amounts that the company stores in its asset accounts. While financial information on these accounts might include receivables collected, the company can also choose to include its contra asset accounts as a separate line item on the balance sheet.
Omicron, South Africa, and how US conspiracy theories fuel vaccine hesitancy Will Bunch – The Philadelphia Inquirer
Omicron, South Africa, and how US conspiracy theories fuel vaccine hesitancy Will Bunch.
Posted: Tue, 30 Nov 2021 15:43:20 GMT [source]
There are many situations where one account is used to offset another account. One common example is accumulated amortisation, which is a contra-asset account. This means that it acts in the opposite manner of a regular asset account. Learn accounting fundamentals and how to read financial statements with CFI’s free online accounting classes. Sales Returns-Sales returns is a Contra Ac of the sales account.
An account with a balance that is the opposite of the normal balance. For example, Accumulated Depreciation is a contra asset account, because its credit balance is contra to the debit balance for an asset account. This is an owner’s equity account and as such you would expect a credit balance. Other examples include the allowance for doubtful accounts, discount on bonds payable, sales returns and allowances, and sales discounts.
A contra account can be used to remedy an error, to track depreciation of an asset, or to register payments that are not collectible. Accumulated DepreciationThe accumulated depreciation of an asset is the amount of cumulative depreciation charged on the asset from its purchase date until the reporting date. It is a contra-account, the difference between the asset’s purchase price and its carrying value on the balance sheet. A contra account is a general ledger account with a balance that is opposite of the normal balance for that account classification. The use of a contra account allows a company to report the original amount and also report a reduction so that the net amount will also be reported. The net amount is often referred to as the carrying amount or perhaps the net realizable amount.
Add contra account to one of your lists below, or create a new one. Malcolm Tatum After many years in the teleconferencing industry, Michael decided to embrace his passion for trivia, research, and writing by becoming a full-time freelance writer. Since then, he has contributed articles to a variety of print and online publications, including , and his work has also appeared in poetry collections, devotional anthologies, and several newspapers. Malcolm’s other interests include collecting vinyl records, minor league baseball, and cycling. Simultaneously, allowance for doubtful debt account shows a closing balance of $5,000.
Author: Loren Fogelman









